搜索结果: 1-15 共查到“农学 Global”相关记录59条 . 查询时间(0.171 秒)

2024年12月29日,中国科学院动物研究所赵莉蔺研究员团队在生态学国际期刊Global Change Biology在线发表了题为“Vulnerability of global pine forestry's carbon sink to an invasive pathogen-vector system”的研究成果,揭示了松材线虫对全球森林碳汇造成威胁。

干旱区约占地球陆地面积的 41%,近几十年来由于全球气候变化和人类活动的影响干旱区面积大幅扩张,了解当前干旱区的气候变化和干旱加剧如何影响植物-土壤系统的全球生物地球化学问题至关重要。因此,亟待一项关于干旱加剧和干旱区扩张对碳储存量、生物多样性丧失和生态系统服务的影响的全面概述。
The Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation: High-resolution laser ranging of the Earth’s forests and topography
lidar ecosystem structure GEDI biomass
2024/1/22
Obtaining accurate and widespread measurements of the vertical structure of the Earth’s forests has been a long-sought goal for the ecological community. Such observations are critical for accurately ...
Thermal Remote Sensing for Global Volcano Monitoring: Experiences From the MIROVA System
thermal remote sensing global volcano monitoring MIROVA MODIS thermal unrest eruption forecasting
2024/1/12
Volcanic activity is always accompanied by the transfer of heat from the Earth's crust to the atmosphere. This heat can be measured from space and its measurement is a very useful tool for detecting v...
Agroforestry to Achieve Global Climate Adaptation and Mitigation Targets: Are South Asian Countries Sufficiently Prepared?
agroforestry South Asia climate change mitigation adaptation policy REDD+ national determined contributions climate neutrality
2024/1/10
Traditional agroforestry systems across South Asia have historically supported millions of smallholding farmers. Since, 2007 agroforestry has received attention in global climate discussions for its c...
Climate Change Risks to Global Forest Health: Emergence of Unexpected Events of Elevated Tree Mortality Worldwide
global forests dynamic global vegetation models forecasting forest assessment remote sensing mortality mechanisms hotter drought
2023/11/30
Recent observations of elevated tree mortality following climate extremes, like heat and drought, raise concerns about climate change risks to global forest health. We currently lack both sufficient d...
2023年11月14日,沈阳农业大学土地与环境学院汪景宽教授和丁凡副教授团队在全球变化生物学领域国际顶级期刊Global Change Biology(5年影响因子12.3)发表题为“A stoichiometric approach to estimate sources of mineral-associated soil organic matter”的文章。丁凡副教授、汪景宽教授为论文共同...
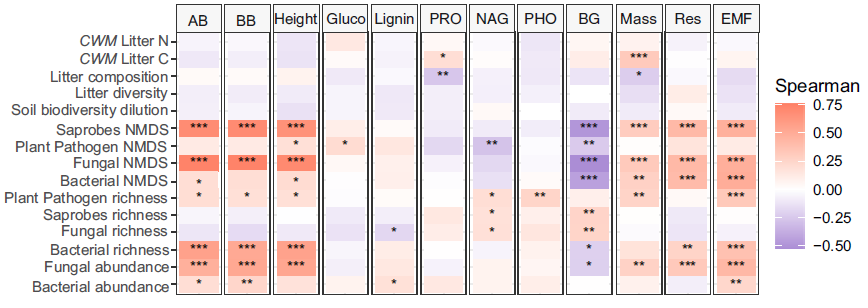
Global Change Biology∣福建农林大学全球气候变化与亚热带森林可持续经营研究团队发表有关生态系统多功能维持机制最新研究(图)
凋落物 土壤生物 多样性 生态系统功能
2023/11/27
近日,福建农林大学林学院刘圣恩老师在环境生态学权威期刊Global Change Biology(全球变化生物学)上发表名为"Litter and soil biodiversity jointly drive ecosystem functions"(“凋落物和土壤生物多样性共同驱动生态系统功能”)的学术论文,报道了凋落物分解过程中地上-地下生物多样性对生态系统多功能性维持机制的研究成果。该团队...

湿地作为“山水林田湖草沙”生命共同体的重要组成部分,是陆地生态系统中重要的碳库,在全球碳循环中发挥着重要作用。在“碳中和”背景下,精准估算湿地土壤有机碳库现状并了解其变化特征具有重要的科学价值。然而,受土壤有机碳密度样本数量有限、湿地空间分布数据不统一、估算方法多采用简单的清单法或线性插值等因素限制,已有的大尺度湿地土壤有机碳库估算结果不确定性较大,无法准确揭示湿地土壤有机碳的空间格局和储量变化特...

宁夏大学生态环境学院荒漠生物多样性团队硕士毕业生在国际顶级期刊Global Change Biology上发表最新研究成果(图)
青藏高原 线虫群落 功能多样性 灌木 降雨量 相互作用
2024/6/27
日前,宁夏大学生态环境学院荒漠生物多样性科研团队刘任涛研究员指导的硕士毕业生张安宁同学在国际顶级期刊Global Change Biology(IF=13.2),以“Shrubs and precipitation interactions shape functional diversity of nematode communities on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau...

中国科学院亚热带农业生态研究所苏以荣研究员团队在我国东部四个水稻分布气候区(中温带-黑土、暖温带-潮土、亚热带-红壤和热带-砖红壤)采用配对采样原则,随机采集了240对稻田和旱地表层土壤。分析发现,四个区域稻田土壤有机碳固持效率比相邻旱地土壤高39%~127%,且以温暖区(亚热带和热带)差异大于寒冷区(中温带和暖温带)。进一步随机选择40对土壤,基于生物标识物木质素和氨基糖分析,量化植物残体和微生...

Global cooling event 4,200 years ago spurred rice's evolution, spread across Asia(图)
Global cooling event 4,200 years ago spurred rice evolution spread across Asia
2020/6/5
A major global cooling event that occurred 4,200 years ago may have led to the evolution of new rice varieties and the spread of rice into both northern and southern Asia, an international team of res...

Global cooling event 4,200 years ago spurred rice's evolution, spread across Asia(图)
Global cooling event 4,200 years ago spurred rice evolution spread across Asia
2020/5/29
A major global cooling event that occurred 4,200 years ago may have led to the evolution of new rice varieties and the spread of rice into both northern and southern Asia, an international team of res...
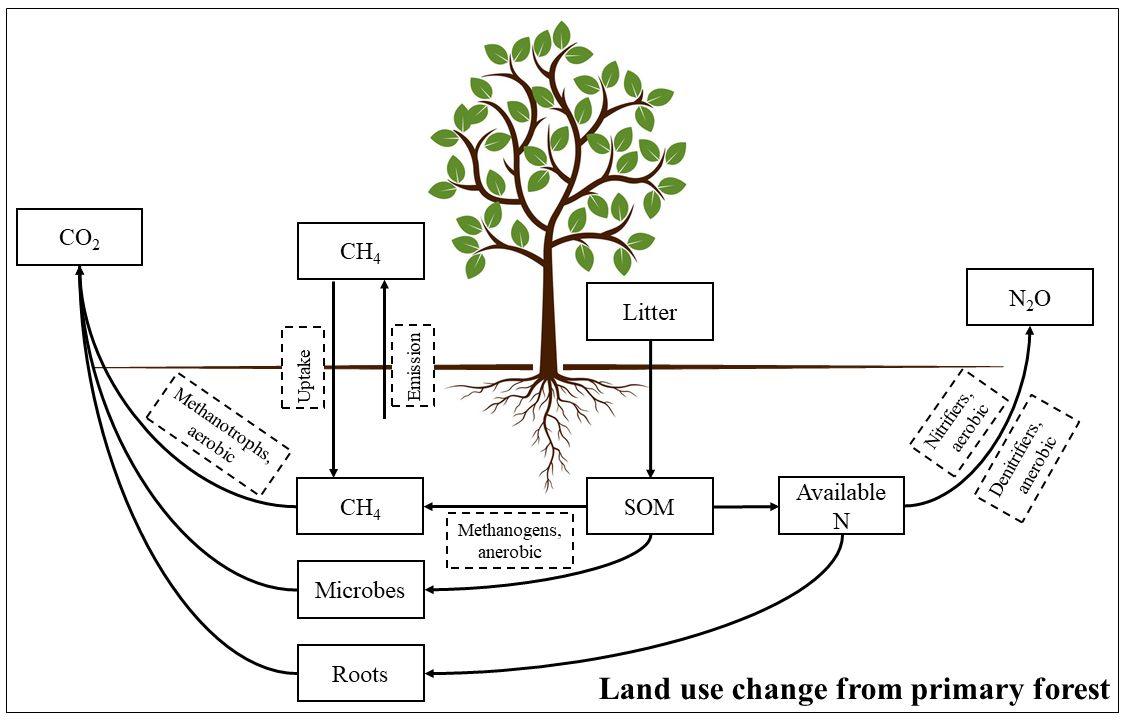
北京大学城市与环境学院朱彪课题组在Global Change Biology发表论文——揭示原始森林土地利用变化对土壤温室气体排放的影响(图)
北京大学城市与环境学院 朱彪 课题组 原始森林 土地利用变化 土壤 温室气体排放
2020/1/22
土地利用改变是全球变化问题的重要组成之一,是导致未来温室效应加剧的关键因素,仅次于化石燃料燃烧。随着人类干扰与气候变化的加剧,全球范围内大面积的原始森林转变为其它植被类型,如人工林、草地和农田等;由此导致的物种组成、植被生产力、土壤有机碳储量等的改变可能会对土壤温室气体(CO2、N2O和CH4)排放产生巨大的影响。北京大学城市与环境学院朱彪课题组通过meta分析的手段系统探讨了全球范围内原始森林土...
Important role of forest disturbances in the global biomass turnover and carbon sinks
CLIMATE FIRE TIME MANAGEMENT DYNAMICS BOREAL IMPACT STOCK MAP
2024/2/5
Forest disturbances that lead to the replacement of whole tree stands are a cornerstone of forest dynamics, with drivers that include fire, windthrow, biotic outbreaks and harvest. The frequency of di...

