搜索结果: 1-6 共查到“知识要闻 AIDS”相关记录6条 . 查询时间(0.109 秒)
人芽囊原虫和贝氏等孢球虫是HIV/AIDS患者常见的机会性肠道寄生原虫。本研究对来自广西地区HIV/AIDS患者的285份粪便样本,基于SSU rRNA基因和ITS-1基因进行人芽囊原虫和贝氏等孢球虫检测及基因特征分析。结果,人芽囊原虫和贝氏等孢球虫的检出率分别为6.0%(17/285)和1.1%(3/285)。鉴定到4种人芽囊原虫亚型,其中ST3(n=8)和ST1(n=6)为优势亚型,其次是ST...
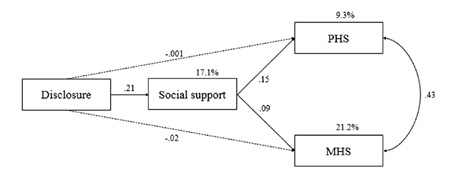
北京大学心理与认知科学学院周广玉课题组在Current Psychology上发表论文揭示HIV/AIDS感染者向家人披露感染情况与生活质量之间的可能路径(图)
HIV/AIDS感染者 披露感染情况 生活质量
2021/7/21
北京大学心理与认知科学学院周广玉研究员课题组的研究成果“The association between HIV disclosure to family members and quality of life among people living with HIV/AIDS: The indirect effects through social support”在Current Psychol...
Study of Hurricane Harvey flooding aids in quantifying climate change
hydraulic model climate change extreme weather
2021/8/4
Researchers used a hydraulic model to consider the degree to which human-caused climate change may have affected flooding in Houston in 2017 during Hurricane Harvey. Resources were used to quantify th...
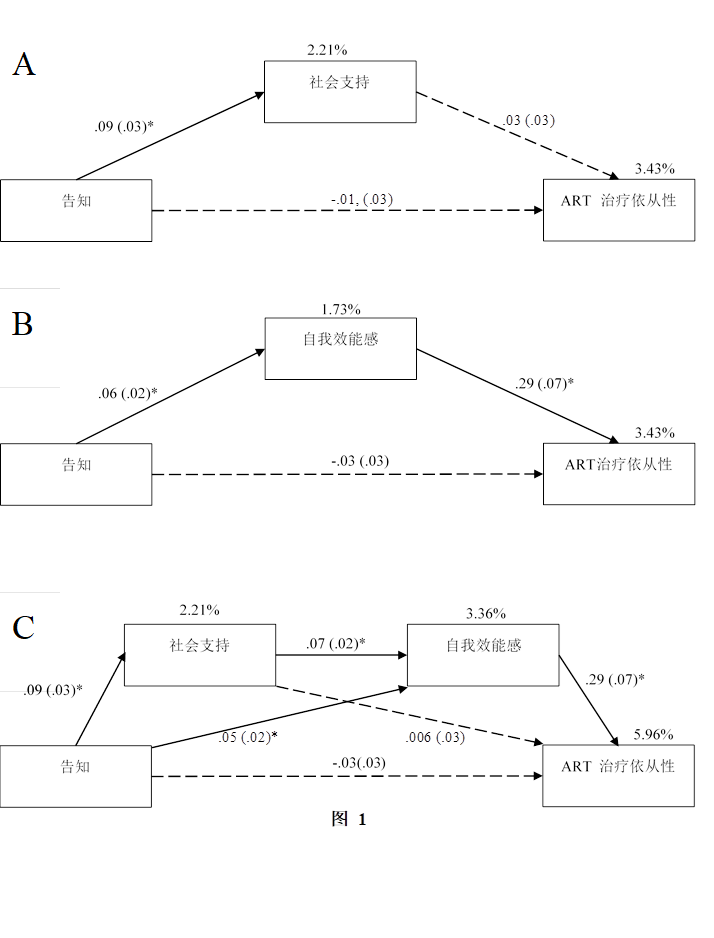
北京大学心理与认知科学学院周广玉课题组在《AIDS and Behavior》发表论文——揭示HIV感染者的病情告知对服药依从性的影响机制(图)
北京大学心理与认知科学学院 HIV感染者 病情告知 服药依从性 影响机制
2020/3/4
2020年1月14日,《AIDS and Behavior》发表了北京大学心理与认知科学学院周广玉研究员课题组的论文“HIV Disclosure to Family Members and Medication Adherence: Role of Social Support and Self‑efficacy”。该研究揭示了HIV感染者对家庭成员的疾病告知与他们接受抗逆转录病毒治...
本中心近期在国际医学杂志“Evidence Based Complementary and AlternativeMedicine”(影响因子4.774)上发表英文论文一篇。

